Retrofits | Stack Testing | Permitting | Training | Analysis | More Services
Autodesk® Simulation Applications
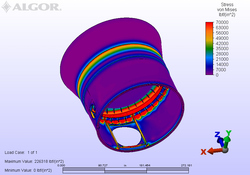
Anticipating Stress Points in Fluidized Bed Incinerator
SITUATION: To determine the stresses in the shell of a fluid bed incinerator if a refractory dome and tuyeres were to be installed in place of a steel tuyere system and support plate.
ANALYSIS: It was determined that the existing shell, having not been designed to support the very large thrusts resulting from a refractory dome, would require excessive reinforcement to withstand the higher stresses. Instead, a new steel pipe tuyere system was proposed to improve reliability and utilize the existing reactor shell. |
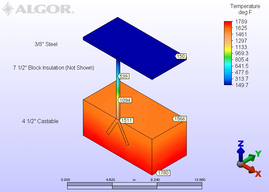
Choosing Anchor Support Material for Castable Refractory
SITUATION: To determine the best choice for material of construction for steel anchors to be used to support heavy castable refractory, in high temperature service in an oxidizing atmosphere.
ANALYSIS: The anchor and the stud would be joined at the interface of the castable and the block insulation, where the temperature was calculated to be 1,511°F. This required the use of high heat resistant stainless steel alloys for both the anchor and the stud, to withstand the stresses and accelerated oxidation resulting from high temperature in an oxidizing atmosphere. |
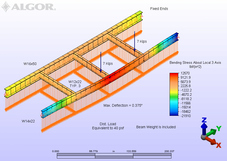
Determining Load Bearing Capacity
SITUATION: To determine the load bearing capacity of existing steel roof beams to be used to hoist materials during a construction project.
ANALYSIS: It was found that stresses in the loaded beams could get uncomfortably close to the allowable yield. Two support points had to be used in this case to assure that the roof beams were not over stressed. |
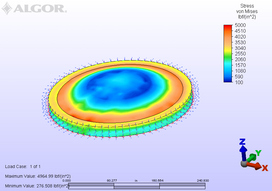
Calculating Hearth Stress at Various Temperatures
SITUATION: To determine the maximum stress in the outermost brick of a circular refractory hearth at varying temperatures.
ANALYSIS: It was determined that the maximum stresses in the skewback bricks were less than the published crushing strengths for the refractory under consideration. In addition, analyses were performed to determine the maximum permissible temperature, beyond which the refractory would likely fail. The radial lines on the illustration represent the direction of movement due to thermal expansion. |
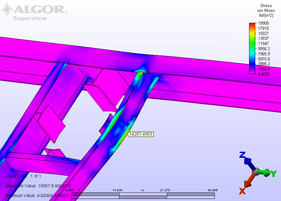
Determining Stress from Wind Due to Stack Extension
SITUATION: To determine if the existing roof structural framing could withstand the additional stresses realized from additional wind loading after extending an existing stack 25 feet. In this illustration the wind loading is in the +Y direction.
ANALYSIS: Stresses in the roof framing did increase and were found to be acceptable under a worst-case condition. It was critical to permit the stack a small amount of lateral movement to minimize the stresses that occur in the stack and the scrubber outlet, if the stack were braced too firmly at the roof opening. |
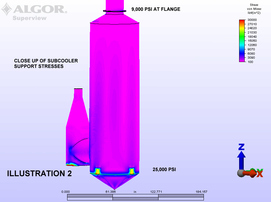
Evaluating Stress Points on Extended Stack Scrubber
SITUATION: To determine the stresses at the discharge of the scrubber exhaust and the scrubber supports when adding 25 feet to the existing stack mentioned above.
ANALYSIS: Stresses in the scrubber outlet flange were kept at a safe level by carefully designing the roof opening for the stack. A calculated amount of stack movement was allowed, thereby minimizing the bending moment on the scrubber outlet resulting from the additional wind loading. Stresses in the scrubber supports were also examined. |